In the realm of education, the term "passive learning" often arises, sparking curiosity and debate. This learning approach, characterized by minimal active engagement from the learner, contrasts sharply with its active counterpart where students take charge of their own learning experiences. Understanding what is passive learning can empower educators, students, and parents to make informed decisions about educational strategies that fit their needs. By examining the intricacies of this concept, we can unveil its significance in the broader context of learning methodologies.
Passive learning encompasses various methods where learners absorb information without direct involvement in the learning process. Think of traditional classrooms where students listen to lectures or watch educational videos without engaging in discussions or hands-on activities. While this method has its critics, it can also offer unique benefits that cater to specific learning environments and styles. In this article, we will explore what is passive learning, its advantages, disadvantages, and its role in the modern education landscape.
As we navigate through this exploration, we will also address common questions surrounding passive learning, such as its effectiveness, when it is most beneficial, and how it compares to active learning techniques. Through this balanced examination, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of passive learning that informs and enlightens readers about its place in today’s educational framework.
What are the Characteristics of Passive Learning?
Passive learning is defined by certain key characteristics that distinguish it from more active forms of learning. These include:
- Minimal interaction between the learner and the material.
- Reliance on listening and observing rather than participating.
- Absence of immediate feedback or collaborative activities.
- Focus on rote memorization and recall of information.
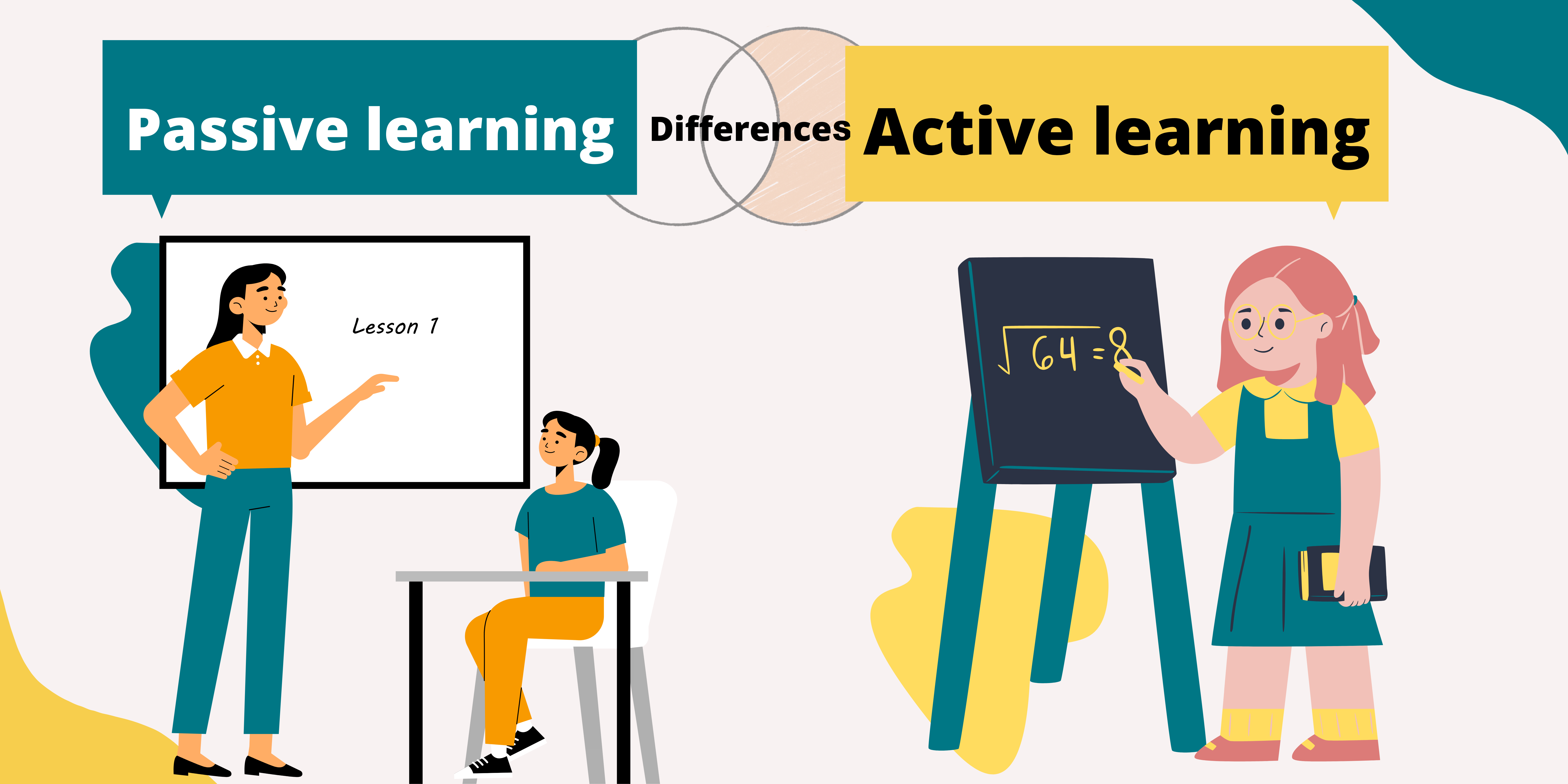
How Does Passive Learning Differ from Active Learning?
To fully grasp what is passive learning, it is essential to compare it with active learning. While passive learning involves the learner being a recipient of information, active learning requires engagement through discussion, problem-solving, and collaboration. Here’s a breakdown of their differences:
Engagement Level
Active learners are involved in their learning process, whereas passive learners absorb content with little to no interaction.
Retention of Information
Studies suggest that active learning leads to better retention of information, while passive learning may result in short-term memory.
What are the Advantages of Passive Learning?
Despite its criticisms, what is passive learning offers several advantages:
- Structured Learning Environment: Passive learning often takes place in structured settings, providing a clear framework for learning.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It can be less resource-intensive, requiring fewer materials and less preparation.
- Accessibility: This method can easily accommodate large groups, making it suitable for classrooms and seminars.
What are the Disadvantages of Passive Learning?
On the flip side, passive learning has its share of drawbacks:
- Limited Critical Thinking: It may not foster the development of critical thinking skills.
- Low Engagement Levels: Students may become disengaged or bored, leading to ineffective learning.
- Knowledge Application: Learners might struggle to apply knowledge in practical situations without hands-on experience.
When is Passive Learning Most Effective?
Understanding when to employ passive learning strategies can enhance their effectiveness. Scenarios where passive learning might be beneficial include:
- Delivering foundational knowledge in a subject.
- Presenting complex information that requires deep comprehension.
- Utilizing multimedia resources for visual or auditory learners.
Can Passive Learning Be Integrated with Active Learning?
Absolutely! What is passive learning can be effectively integrated with active learning strategies to create a more balanced approach. For example:
- Start with a lecture (passive) followed by group discussions (active).
- Use videos to introduce a topic (passive) and then engage students in hands-on projects (active).
Conclusion: The Future of Passive Learning in Education
In conclusion, what is passive learning remains a relevant topic in educational discourse. While it has its limitations, the method can serve as a valuable component in a holistic learning strategy when used appropriately. As educators and learners navigate the complexities of modern education, understanding the role of passive learning will be crucial in fostering an environment conducive to knowledge acquisition and growth.
Article Recommendations
- The Ultimate Guide To Seann William Scott From Stifler To A Star
- The Ultimate Guide To Leslie Easterbrook A Hollywood Icon
- The Definitive Guide To Judd Nelson Exploring The Life And Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon