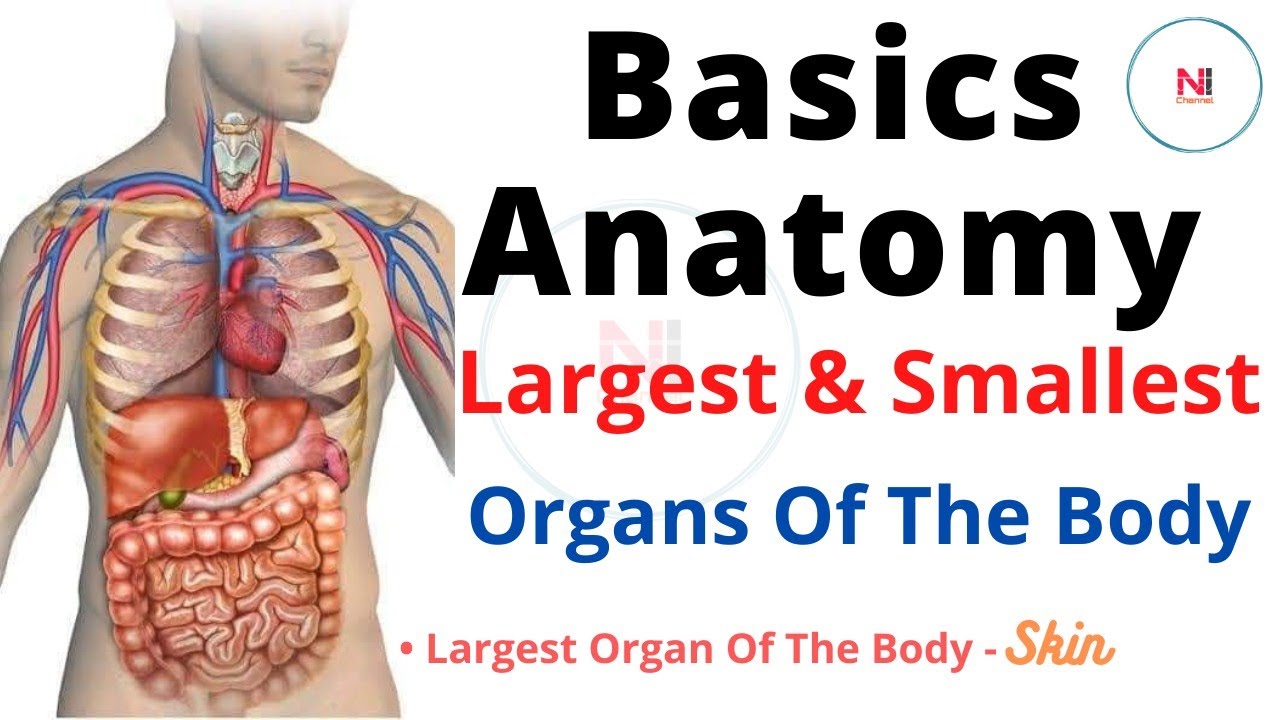
The human body is a remarkable composition of various organs, each playing a crucial role in maintaining our health and well-being. Among these organs, one stands out as the second largest organ in the body, often overshadowed by the skin, which is the largest. This article delves into the intricacies of this vital organ, exploring its functions, importance, and how it contributes to our overall health. Understanding the second largest organ in the body can help us appreciate the complex systems working tirelessly within us. Not only does this organ serve essential functions, but it also reflects our lifestyle choices and overall health status.
As we journey through this exploration, we'll uncover the significance of the second largest organ in the body and how it interacts with other systems. From its role in metabolism to its involvement in detoxification, the importance of this organ cannot be understated. Whether you're a student of biology, a health enthusiast, or just curious about the human body, this article will provide you with valuable insights into one of our most vital organs.
By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of the second largest organ in the body, its functions, and how to keep it healthy. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to uncover the secrets of this often-overlooked organ!
What is the Second Largest Organ in the Body?
The second largest organ in the body is the liver. Weighing about 3 pounds and located in the upper right side of the abdomen, the liver plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It is responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, and storing essential nutrients.
What Functions Does the Liver Serve?
The liver is a multifunctional organ that is vital for maintaining overall health. Here are some of its primary functions:
- Detoxification: The liver filters blood from the digestive tract, removing toxins and harmful substances.
- Metabolism: It plays a key role in converting nutrients from the food we eat into essential substances the body needs.
- Bile Production: The liver produces bile, which is crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats.
- Storage: It stores vitamins, minerals, and glycogen, which can be released into the bloodstream as needed.
How Does the Liver Impact Metabolism?
The liver is central to metabolic processes, including the regulation of blood sugar levels, cholesterol production, and the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It transforms nutrients into energy and ensures that the body has a steady supply of essential substances.
What Are the Signs of Liver Disease?
Liver disease can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the symptoms early can be crucial for effective treatment. Common signs include:
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dark urine and pale stools
How Can We Keep the Liver Healthy?
Maintaining liver health is essential for overall well-being. Here are some tips to support liver function:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help the liver flush out toxins.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage liver cells.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of liver disease.
What Are Common Liver Diseases?
Several diseases can affect the liver, including:
- Hepatitis (inflammation of the liver)
- Cirrhosis (scarring of the liver tissue)
- Fatty liver disease (accumulation of fat in liver cells)
- Liver cancer
What Are Some Interesting Facts About the Liver?
The liver is a fascinating organ with many unique characteristics. Here are some interesting facts:
- The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate itself. Even if a significant portion is removed, it can grow back to its original size.
- It performs over 500 different functions, making it one of the most versatile organs in the body.
- The liver is the only organ that can produce blood-clotting factors.
How Does the Liver Interact with Other Organs?
The liver does not work in isolation; it interacts with several other organs to maintain homeostasis. For example:
- The pancreas works with the liver to regulate blood sugar levels.
- The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver, which is then used for digestion.
- The kidneys filter blood and work alongside the liver in detoxification processes.
Conclusion: Why the Liver is Essential for Life
The liver is undoubtedly the second largest organ in the body and is crucial for our survival. Its multifunctional role in metabolism, detoxification, and nutrient storage highlights its importance in our daily lives. By understanding the liver's functions and how to maintain its health, we can lead healthier lives and avoid potential diseases. Remember, a healthy liver is key to a healthy body!
| Personal Details | Bio Data |
|---|---|
| Name | Not Applicable |
| Function | Metabolism, Detoxification, Bile Production, Storage |
| Weight | Approximately 3 pounds |
| Location | Upper right abdomen |
Article Recommendations
- The Ultimate Guide To Hazel Moder The Next Generation Of Hollywood Star
- The Definitive Guide To Judd Nelson Exploring The Life And Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon
- The Ultimate Guide To Seann William Scott From Stifler To A Star