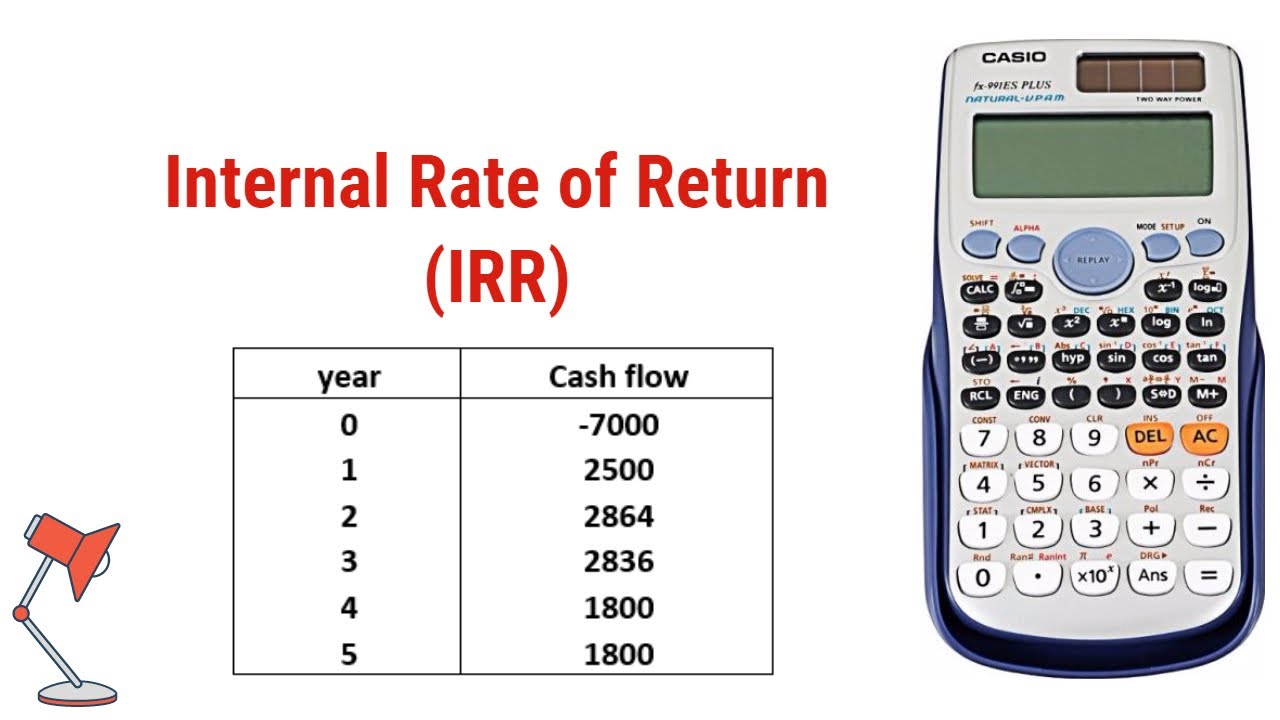
Understanding the intricacies of financial calculations can greatly enhance your investment decision-making process. One of the most pivotal metrics in finance is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR). This percentage represents the annual growth rate earned on an investment over time, taking into account the time value of money. Calculating IRR can seem daunting, especially without the right tools. Fortunately, financial calculators are designed to simplify this process, allowing investors to quickly determine the IRR of various projects and investments.
In this article, we will delve into the step-by-step process of how to calculate IRR in financial calculators. By breaking down the calculation into manageable parts, even those new to finance can grasp the concept and apply it effectively. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a beginner, understanding IRR is crucial for evaluating potential investments and making informed financial decisions.
Join us as we explore the essential techniques and tips for calculating IRR using a financial calculator. By the end of this guide, you will not only understand how to perform the calculation but also how to interpret the results to make better financial choices.
What is IRR and Why is it Important?
IRR, or Internal Rate of Return, is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It is the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of all cash flows from the investment equal to zero. Understanding the importance of IRR can shape your investment strategies.
How Do Financial Calculators Work for IRR Calculations?
Financial calculators are specifically designed to handle complex financial formulas, including IRR calculations. They utilize algorithms to determine the rate at which the present value of cash inflows equals the present value of cash outflows over a specified time period.
What Are the Steps to Calculate IRR in a Financial Calculator?
- Input Cash Flows: Enter the initial investment amount as a negative cash flow followed by the expected cash inflows for subsequent periods.
- Select the IRR Function: Most calculators have a dedicated IRR button; select this function.
- Calculate: Press the calculate button to determine the IRR.
What Inputs Do You Need for IRR Calculation?
To calculate IRR accurately, you'll need to gather specific inputs:
- Initial Investment: The amount of money invested initially (usually a negative number).
- Future Cash Flows: The projected cash inflows for each period.
- Time Periods: The duration over which the cash flows occur.
Can You Calculate IRR Without a Financial Calculator?
While it is possible to calculate IRR manually using mathematical formulas, this approach can be time-consuming and complex. Financial calculators simplify this process by automating calculations and providing quicker results.
How Accurate is IRR in Financial Decisions?
IRR is a useful tool, but it should not be the sole factor in investment decisions. It is essential to consider other metrics such as NPV, payback period, and overall market conditions. Using IRR in conjunction with these metrics can lead to more informed investment choices.
What Are Common Mistakes When Calculating IRR?
Investors often make mistakes when calculating IRR, such as:
- Ignoring Cash Flow Timing: Timing of cash flows can significantly impact IRR calculations.
- Overlooking Negative Cash Flows: Not accounting for all cash outflows can skew results.
- Using IRR Alone: Relying solely on IRR without considering other financial metrics can lead to poor investment decisions.
Conclusion: How to Calculate IRR in Financial Calculator?
In summary, calculating IRR in a financial calculator is a straightforward process that involves inputting cash flows, selecting the IRR function, and performing the calculation. Understanding how to calculate IRR in financial calculator not only streamlines your investment analysis but also enhances your ability to make sound financial decisions. As you grow more familiar with this crucial metric, you'll find that it plays a significant role in assessing the viability of potential investments.
Article Recommendations
- The Marvelous World Of Andrew Stevens
- Jules Ari The Ultimate Guide To Her Music Career And Legacy
- Billionaire In The Making The Rise Of Kathy May Fritz