When it comes to understanding our own bodies, many of us often overlook the incredible complexities and functionalities of our organs. Among these, the largest organ in your body plays a crucial role in not just physical protection but also in various physiological processes. This organ, which often goes unnoticed, is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. In this article, we will dive deep into the significance of the largest organ, its functions, and its impact on our daily lives. By the end, you'll have a greater appreciation for this vital component of your anatomy.
The human body is a fascinating structure, composed of numerous organs that each serve unique purposes. However, understanding what the largest organ in your body is, and its functions, can help demystify the importance of taking care of it. This organ does not just provide a barrier against external threats; it also plays a significant role in regulating body temperature, fluid balance, and even sensations like touch and pain.
As we explore the largest organ in your body, we'll answer several key questions that arise about its structure, functions, and the vital role it plays in our overall health. So, let's embark on this educational journey and uncover the secrets behind this remarkable organ!
What is the Largest Organ in Your Body?
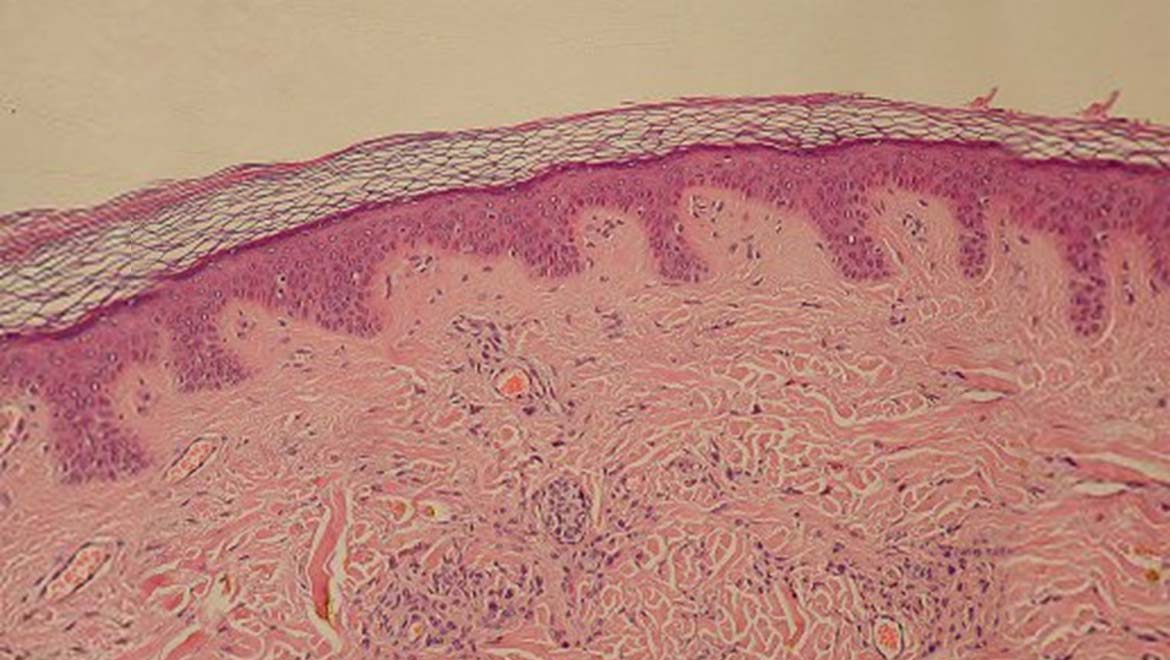
The largest organ in your body is your skin. This incredible organ covers the entire surface of your body and is made up of multiple layers, each serving different purposes. The skin is not only the outermost layer of protection but also plays an essential role in various bodily functions.
Why is Skin Considered an Organ?
Many people are surprised to learn that skin is classified as an organ. The reason for this classification lies in its complexity and the various functions it performs. Like other organs, the skin is composed of multiple cells and tissues that work together to achieve specific goals. Here are a few reasons why skin is considered an organ:
- It contains various types of cells, including epithelial cells, melanocytes, and fibroblasts.
- It has multiple layers, including the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
- It performs essential functions such as protection, sensation, and thermoregulation.
What Are the Functions of Skin?
The skin performs several vital functions that are crucial for our overall health. Here are some of the most important roles that skin plays in the body:
- Barrier Protection: The skin acts as a barrier against pathogens, bacteria, and harmful substances.
- Sensation: It contains nerve endings that help us feel touch, temperature, and pain.
- Thermoregulation: Skin helps regulate body temperature through sweating and blood flow.
- Vitamin D Synthesis: The skin plays a role in producing vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
How Does Skin Change Over Time?
As we age, our skin undergoes various changes that can affect its appearance and function. Understanding these changes can help us better care for our skin throughout our lives.
What Are the Signs of Aging Skin?
Here are some common signs of aging skin:
- Wrinkles and fine lines.
- Loss of elasticity and firmness.
- Dryness and uneven texture.
- Age spots and discoloration.
How Can We Care for Our Skin?
Caring for your skin is essential for maintaining its health and appearance. Here are some tips for effective skin care:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Use sunscreen to protect against UV damage.
- Moisturize regularly to prevent dryness.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants.
What Happens If You Neglect Your Skin?
Neglecting your skin can lead to various issues that may affect not only its appearance but also overall health. Here are some potential consequences of inadequate skin care:
- Increased risk of skin infections.
- Premature aging and wrinkles.
- Development of skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
- Higher likelihood of skin cancer due to sun exposure.
Can Skin Reflect Internal Health?
Indeed, skin can be a mirror of our internal health. Changes in skin appearance can indicate underlying health issues. For example:
- Acne may signal hormonal imbalances.
- Yellowing skin can indicate liver problems.
- Dry or flaky skin may be a sign of dehydration or thyroid issues.
How Can You Keep Your Skin Healthy?
Maintaining healthy skin is a lifelong commitment. Here are some additional tips for keeping your skin in top shape:
- Regularly visit a dermatologist for check-ups.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
- Practice stress management techniques to reduce skin flare-ups.
Conclusion: Embrace Your Largest Organ
Understanding what's the largest organ in your body is an essential step toward appreciating the incredible complexity of human anatomy. Your skin, as the largest organ, serves numerous vital functions that contribute to your overall health and well-being. By taking proactive steps to care for your skin, you can ensure that it remains healthy and vibrant throughout your life. Remember, your skin is not just a covering; it is a vital organ that deserves your attention and care!
Article Recommendations
- The Definitive Guide To Judd Nelson Exploring The Life And Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon
- Meet Accomplished Leader Jennifer Grant
- Billionaire In The Making The Rise Of Kathy May Fritz