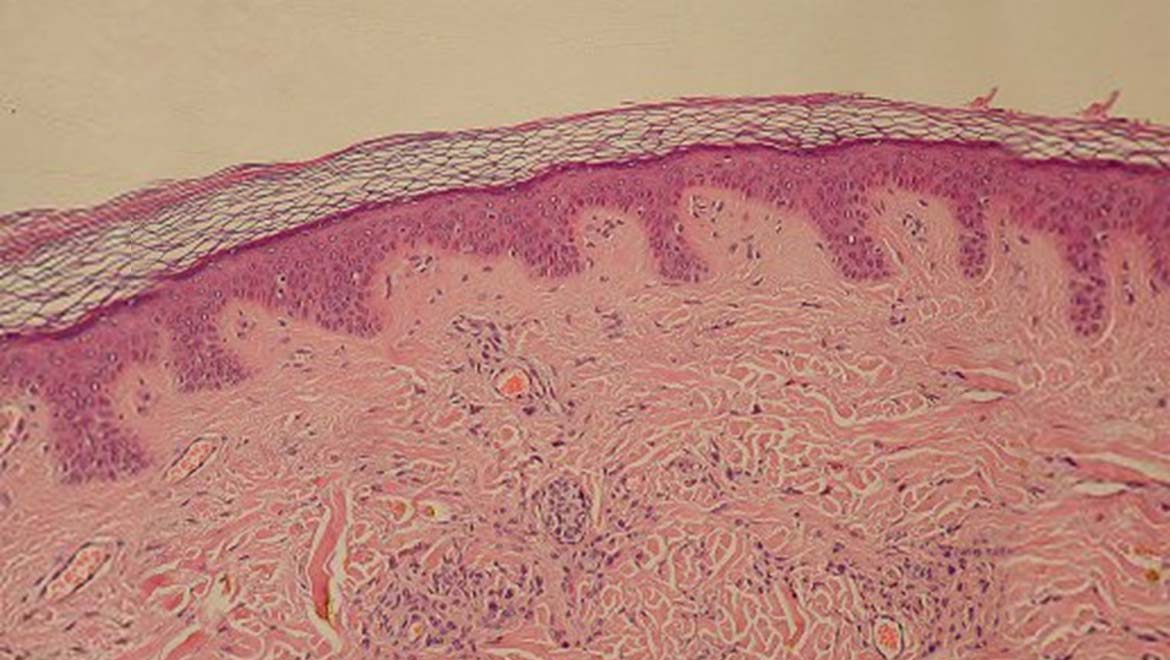
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, composed of various organs that work together to maintain health and functionality. Among these organs, one stands out as the largest and perhaps the most vital: the skin. This remarkable organ serves numerous purposes, from protecting our internal structures to regulating body temperature and facilitating the sense of touch. Understanding the largest organ in the body reveals not only its anatomical significance but also its critical role in our overall well-being.
In addition to its size, the skin is a marvel of biological engineering. It consists of multiple layers, each with specific functions and properties. The outermost layer, the epidermis, acts as a barrier against environmental threats, while the underlying dermis contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue that support the skin's structure. The skin not only serves as a protective shield but also plays a crucial role in our sensory perception, allowing us to experience the world around us.
Moreover, the largest organ in the body is also a dynamic entity, undergoing constant renewal and repair. Every day, our skin cells shed and are replaced, demonstrating the body's incredible ability to heal and adapt. This article aims to explore the intricacies of the skin, its functions, and the importance of caring for this vital organ to maintain our health and vitality.
What Makes the Skin the Largest Organ in the Body?
The human skin is the largest organ in the body, encompassing a surface area of approximately 1.5 to 2 square meters in adults. It accounts for about 15% of our total body weight and has a thickness that varies across different regions of the body. The skin's primary function is to act as a protective barrier against external threats, including pathogens, chemicals, and physical injuries.
How Many Layers Does the Skin Have?
The skin is made up of three main layers:
- Epidermis: The outermost layer, which provides a waterproof barrier and skin tone.
- Dermis: The middle layer, containing connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
- Hypodermis: The deepest layer, composed of fat and connective tissue that insulates the body and absorbs shocks.
What Are the Functions of the Largest Organ in the Body?
The skin performs several essential functions, including:
- Protection: Shields against environmental hazards, including bacteria and UV radiation.
- Regulation: Maintains body temperature through sweating and blood flow adjustments.
- Sensation: Contains nerve endings that provide the sense of touch, heat, and pain.
- Vitamin D Synthesis: The skin helps produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, which is crucial for bone health.
How Does Skin Health Impact Overall Well-Being?
The health of our skin is a direct reflection of our overall health. Conditions such as stress, poor nutrition, and lack of hydration can manifest as skin issues. Furthermore, skin problems can also lead to psychological effects, such as low self-esteem and anxiety. Therefore, taking care of our skin is not just about aesthetics; it is essential for our emotional and mental well-being.
What Are Common Skin Conditions to Be Aware Of?
Some common skin conditions include:
- Acne: A prevalent condition affecting many, often caused by hormonal changes and blocked pores.
- Eczema: A chronic condition characterized by inflamed, itchy skin.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune disorder that results in the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to scaling and inflammation.
- Rosacea: A condition that causes redness and visible blood vessels, often affecting the face.
How Can You Maintain Healthy Skin?
To maintain the health of the largest organ in the body, consider the following tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated from the inside out.
- Use Sunscreen: Protect your skin from harmful UV rays by applying sunscreen daily.
- Follow a Healthy Diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats to nourish your skin.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regularly cleanse your skin to remove dirt and prevent breakouts.
What Are the Myths Surrounding Skin Care?
There are numerous myths about skin care that can lead to misconceptions about the largest organ in the body. Some common myths include:
- Myth 1: "Oily skin doesn't need moisturizer." (In fact, all skin types benefit from hydration.)
- Myth 2: "Sunscreen is only necessary on sunny days." (UV rays can penetrate clouds.)
- Myth 3: "Natural products are always better for your skin." (Not all natural ingredients are safe for everyone.)
What Role Does Skincare Play in Aging?
As we age, our skin undergoes significant changes, including a decrease in collagen production and the appearance of wrinkles. Effective skincare can help slow down the aging process and maintain a youthful appearance. Key components of an anti-aging regimen may include:
- Retinoids: Promote cell turnover and collagen production.
- Antioxidants: Protect the skin from free radical damage.
- Moisturizers: Keep the skin hydrated and plump.
- Sunscreen: Prevents sun damage, which accelerates aging.
What Are the Future Innovations in Skin Health?
As research continues, the future of skin health looks promising. Innovations in dermatology and skincare products aim to enhance the health of the largest organ in the body. Some exciting developments include:
- Personalized Skincare: Tailoring products to individual skin types and concerns.
- Gene Therapy: Potential treatments for genetic skin disorders.
- Wearable Technology: Devices that monitor skin health in real-time.
In conclusion, the largest organ in the body, the skin, plays a vital role in protecting our health and reflecting our overall well-being. Understanding its structure, functions, and the importance of proper care can empower us to take proactive steps toward maintaining healthy skin throughout our lives.
Article Recommendations
- The Ultimate Guide To Hazel Moder The Next Generation Of Hollywood Star
- Meet Accomplished Leader Jennifer Grant
- Uncover The Truth About Health A Conversation With Dr Jane Ruby