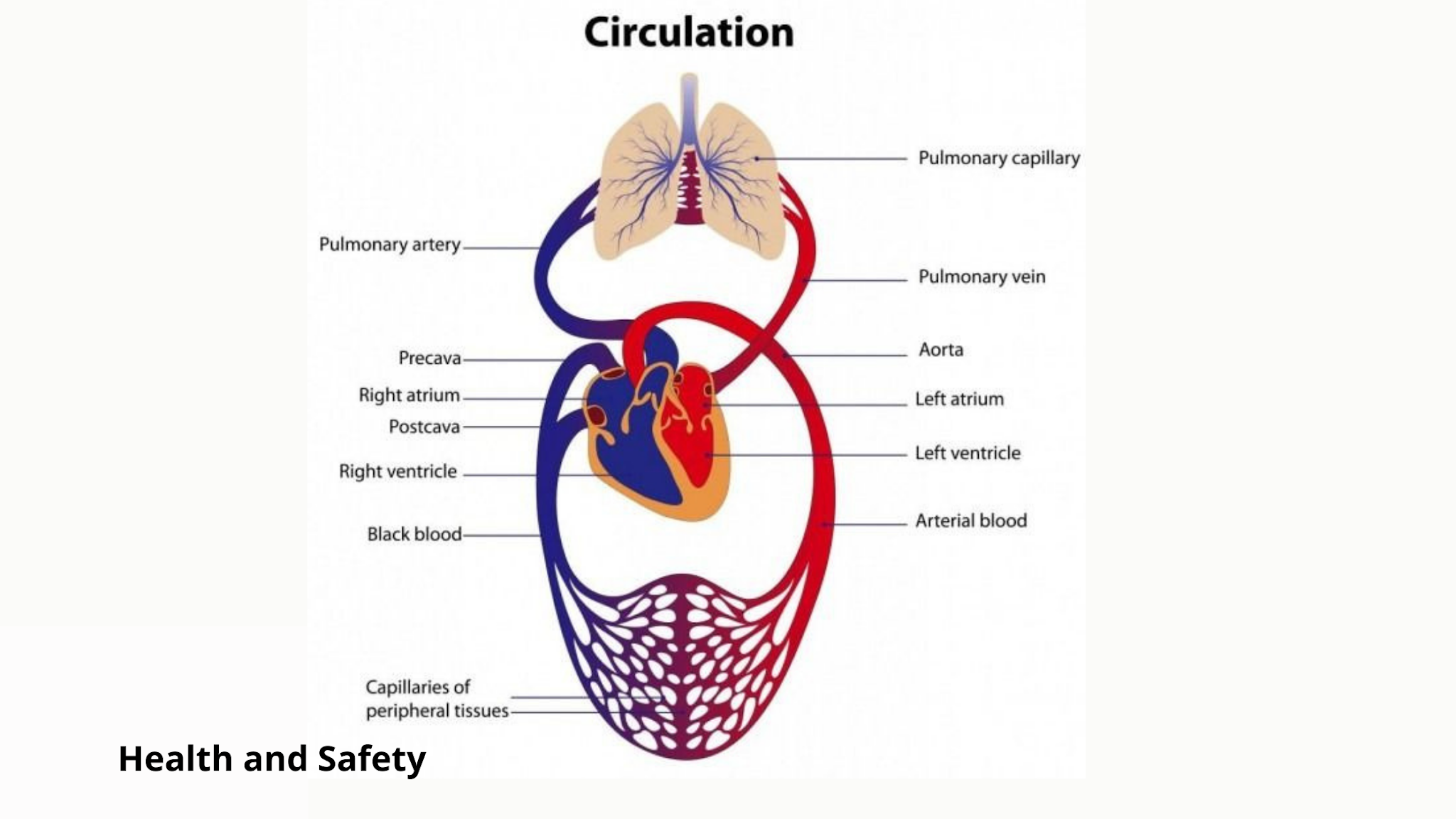
The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, with various systems working in harmony to sustain life. Among these systems, the respiratory and circulatory systems stand out as essential players in the intricate dance of life. Together, they ensure that oxygen reaches every cell in the body while simultaneously removing carbon dioxide, a byproduct of cellular respiration. In this article, we will explore the critical relationship between these two systems, shedding light on how they collaborate to maintain homeostasis and support overall health.
The respiratory system is responsible for the intake of oxygen and the expulsion of carbon dioxide. It includes vital organs such as the lungs, trachea, and diaphragm. On the other hand, the circulatory system transports blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs while carrying away waste products. The connection between these two systems is fundamental to our survival; they rely on each other to function correctly. Understanding how respiratory system and circulatory system work together can provide insights into how our bodies respond to various conditions and challenges.
As we delve deeper into this fascinating subject, we will answer some critical questions about the roles of these systems, the processes that enable their cooperation, and the implications for our health. By grasping the interplay between the respiratory and circulatory systems, we can better appreciate the complexity of our biology and the importance of maintaining these systems for overall well-being.
What is the Role of the Respiratory System?
The respiratory system plays a crucial role in the process of breathing, which is essential for life. Its primary functions include:
- Facilitating gas exchange: Oxygen enters the body while carbon dioxide is expelled.
- Regulating blood pH: Carbon dioxide levels affect the acidity of the blood.
- Protecting against pathogens: The respiratory system traps and removes harmful substances.
- Providing vocalization: The larynx and vocal cords enable speech and communication.
How Does the Circulatory System Function?
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system, is responsible for transporting blood throughout the body. Its key components include:
- The heart: The muscular organ that pumps blood.
- Blood vessels: Arteries, veins, and capillaries that carry blood to and from the heart.
- Blood: The fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
How Do the Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Work Together?
The interplay between the respiratory and circulatory systems is vital for maintaining life. Here’s how they collaborate:
- Oxygen Intake: The respiratory system takes in oxygen from the air.
- Gas Exchange: Oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream through the alveoli in the lungs.
- Transportation: The circulatory system carries oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart.
- Distribution: Blood is pumped from the heart to various tissues and organs.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Carbon dioxide is transported back to the lungs for exhalation.
What Happens During Gas Exchange?
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, tiny air sacs within the lungs. This process involves:
- Inhalation: Air rich in oxygen enters the lungs.
- Diffusion: Oxygen passes from the alveoli into the blood while carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction.
- Exhalation: Carbon dioxide is expelled from the lungs, completing the cycle.
How is Oxygen Transported in the Blood?
Once oxygen enters the bloodstream, it binds to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. This process ensures efficient transport to tissues throughout the body. Here’s how it works:
- Oxygen binds to hemoglobin in the lungs.
- Oxygen-rich blood travels through the circulatory system.
- Oxygen is released to cells where it is needed for energy production.
What is the Importance of Maintaining Healthy Respiratory and Circulatory Systems?
Maintaining the health of both systems is crucial for overall well-being. Some tips include:
- Regular exercise to strengthen the heart and lungs.
- A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients.
- Avoiding smoking and exposure to pollutants.
- Regular check-ups to monitor cardiovascular and respiratory health.
How Do Diseases Affect the Interplay Between These Systems?
Diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and heart conditions can disrupt the function of the respiratory and circulatory systems. It is essential to understand how these diseases interfere with their collaboration:
- Asthma: Narrowed airways lead to reduced airflow and oxygen intake.
- COPD: Damage to lung tissues impairs gas exchange.
- Heart Disease: Reduced blood flow can limit oxygen delivery to tissues.
What Are the Implications for Overall Health?
The interconnectedness of the respiratory and circulatory systems means that issues in one can lead to complications in the other. For instance, a respiratory infection can lead to reduced oxygen levels in the blood, putting a strain on the heart. Understanding how respiratory system and circulatory system work together can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical intervention.
Conclusion
In summary, the respiratory and circulatory systems are two vital components of the human body that work together seamlessly to sustain life. Their cooperation ensures that oxygen reaches every cell while removing carbon dioxide, emphasizing the importance of maintaining these systems for overall health. By understanding their functions and interdependence, we can take proactive steps toward a healthier lifestyle.
Article Recommendations
- Vegamoviestoo The Ultimate Movie Streaming Destination
- The Ultimate Goojara Movies Experience Explore A World Of Entertainment
- The Ultimate Guide To Leslie Easterbrook A Hollywood Icon