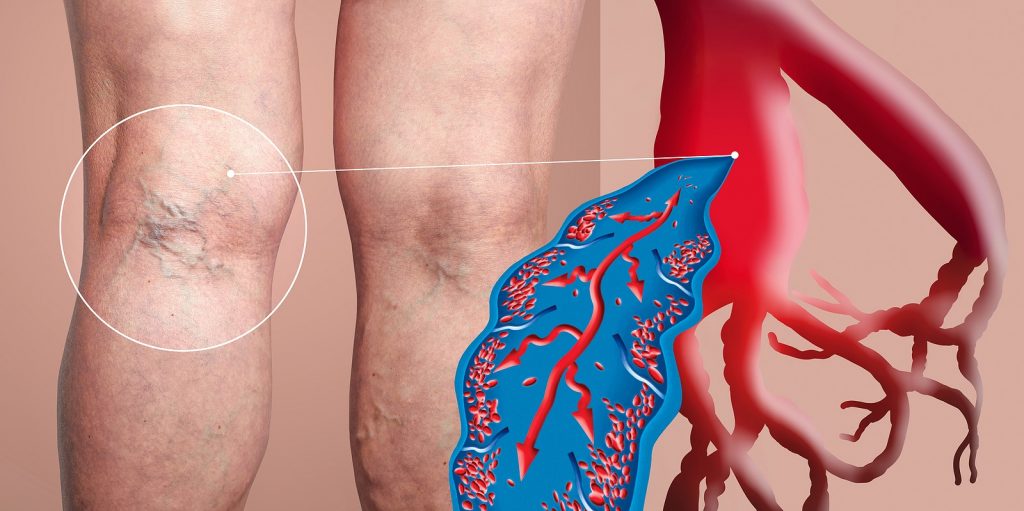
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, often in the legs. This condition can lead to significant complications, including pulmonary embolism, which can be life-threatening. The ICD-10 coding system provides healthcare professionals with the necessary framework to accurately diagnose, document, and treat DVT. Understanding the intricacies of ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis can empower patients and providers alike to navigate this complex condition effectively.
As we delve into the realm of DVT, it's essential to recognize the critical role that accurate coding plays in patient management and healthcare reporting. The ICD-10 system, which stands for the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, is widely used by healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures. This coding is vital for billing, statistical analysis, and research purposes. Therefore, being informed about ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis can enhance patient care and ensure that individuals receive the appropriate treatment and resources they need.
Moreover, with the rise of telehealth and digital health records, understanding ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis is more important than ever. Healthcare providers must be able to communicate effectively about diagnoses and treatment plans, and accurate coding lends clarity to these discussions. Patients who are knowledgeable about their conditions and the corresponding codes can advocate for themselves within the healthcare system. In this article, we will explore various aspects of ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis, including its classification, symptoms, treatment options, and the implications of accurate coding for patients and healthcare providers.
What is ICD-10 Deep Vein Thrombosis?
ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis refers to the specific code assigned within the ICD-10 classification system for diagnosing DVT. The codes help healthcare providers accurately document the occurrence of blood clots in deep veins, primarily in the legs. The specific ICD-10 codes for DVT vary depending on the location and characteristics of the clot. For example, the ICD-10 code I82.4 refers to deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities. By understanding these codes, healthcare providers can improve the accuracy of their diagnoses and ensure appropriate treatment protocols are followed.
What Are the Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Recognizing the symptoms of deep vein thrombosis is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling in one leg
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Warmth in the skin over the affected vein
- Red or discolored skin
However, some individuals may experience DVT without any noticeable symptoms, making it essential for at-risk populations to undergo regular screenings and assessments.
Who Is at Risk for Developing Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Several factors can increase an individual's risk of developing deep vein thrombosis, including:
- Prolonged immobility (e.g., long flights or bed rest)
- Recent surgery or injury
- Obesity
- Pregnancy or recent childbirth
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., cancer, heart disease)
Being aware of these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek medical attention when necessary.
How is Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing deep vein thrombosis typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Common diagnostic procedures include:
- Doppler ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of blood flow in the veins.
- CT or MRI scans: Advanced imaging techniques that provide detailed views of the veins and surrounding structures.
- Blood tests: Tests such as D-dimer can help assess the likelihood of clot formation.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and preventing complications.
What Are the Treatment Options for Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Treatment for deep vein thrombosis typically involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes procedures to remove the clot. Common treatment options include:
- Anticoagulants: Medications that help prevent the formation of new clots and reduce the size of existing clots.
- Thrombolytics: Medications that dissolve blood clots, typically used in more severe cases.
- Compression stockings: Specialized stockings that help reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove a clot or place a filter in the vein.
Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their individual circumstances.
How Does Accurate Coding Impact Patient Care?
Accurate coding of ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis is pivotal for several reasons:
- Billing and Reimbursement: Correct coding ensures that healthcare providers are adequately reimbursed for their services.
- Quality of Care: Accurate documentation allows for better tracking of patient outcomes and treatment efficacy.
- Research and Public Health: Aggregated data from accurate coding can inform public health initiatives and research efforts.
Patients benefit from accurate coding through improved communication and understanding of their conditions, leading to better health outcomes.
What Can Patients Do to Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Preventive measures are essential for reducing the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis. Patients can take the following steps:
- Stay active and incorporate regular physical activity into daily routines.
- Avoid prolonged periods of immobility; take breaks during long trips or flights.
- Maintain a healthy weight and eat a balanced diet.
- Discuss risk factors with healthcare providers, especially before surgeries or during pregnancy.
By being proactive, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of DVT and its complications.
Conclusion: Understanding ICD-10 Deep Vein Thrombosis
In summary, ICD-10 deep vein thrombosis is an essential topic for both healthcare providers and patients. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of accurate coding, individuals can better navigate this complex medical condition. Armed with knowledge, patients can advocate for themselves and work collaboratively with their healthcare providers to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Article Recommendations
- Vegamoviestoo The Ultimate Movie Streaming Destination
- The Definitive Guide To Judd Nelson Exploring The Life And Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon
- Steamunlocked Download Cracked Games Free