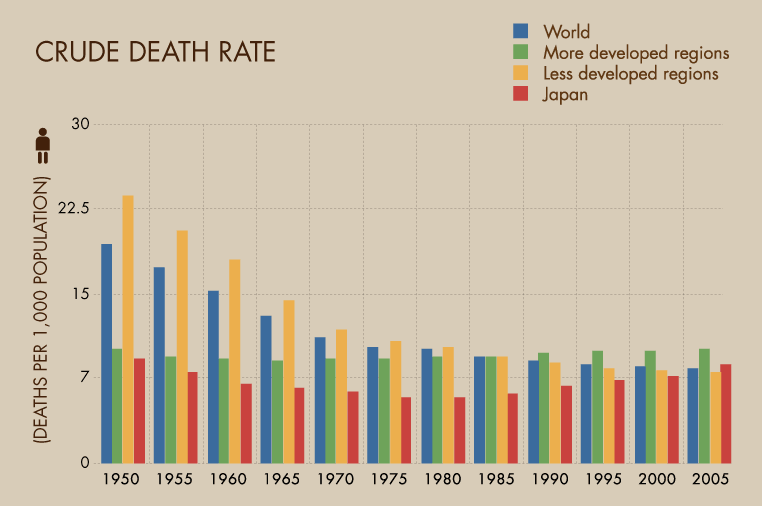
The crude death rate is a vital statistic that helps demographers, public health officials, and policymakers assess the overall health of populations. It provides a snapshot of mortality in a given area, reflecting not just the number of deaths but also the factors influencing these deaths. By analyzing crude death rates, we can better understand the impacts of diseases, healthcare access, environmental factors, and social conditions on a population's well-being.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the definition of crude death rate, how it is calculated, and its significance in public health and demographic studies. We will explore various aspects of this metric, including its historical context and applications in contemporary research. Understanding the crude death rate is essential for interpreting health data and making informed decisions regarding health policies and resource allocation.
Moreover, as we explore the intricacies surrounding the crude death rate, we will also address common questions and misconceptions about this crucial indicator. From understanding its limitations to interpreting its implications, we will provide a comprehensive overview that will enhance your understanding of this essential metric.
What is the Crude Death Rate?
The crude death rate (CDR) is a demographic measure that represents the number of deaths in a given population during a specific time frame, typically expressed per 1,000 individuals. It serves as a broad indicator of mortality and is calculated using the following formula:
Crude Death Rate = (Number of Deaths / Total Population) × 1,000
This straightforward calculation allows for relatively easy comparisons between different populations or regions, although it does not account for age distribution or other demographic factors that can significantly affect mortality rates.
Why is the Crude Death Rate Important?
The crude death rate plays a crucial role in various fields, including public health, sociology, and demography. Here are some reasons why it is important:
- Public Health Assessment: CDR provides insights into the health status of a population, allowing health officials to identify trends and potential health crises.
- Policy Development: Policymakers can utilize CDR data to allocate resources effectively and develop interventions aimed at reducing mortality.
- International Comparisons: CDR serves as a useful tool for comparing health outcomes across different countries or regions.
- Historical Analysis: By examining changes in CDR over time, researchers can gain insights into the effectiveness of public health initiatives and societal changes.
How is the Crude Death Rate Calculated?
The calculation of the crude death rate is relatively simple, as outlined earlier. However, understanding the data sources and methodologies behind the numbers is essential for accurate interpretation. The total number of deaths is typically sourced from vital statistics systems, which compile data from death certificates. This is then divided by the total population, which can be estimated through census data or population registries.
It is important to note that the crude death rate can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Age Structure: Populations with a higher proportion of elderly individuals tend to have higher crude death rates.
- Healthcare Access: Countries or regions with better healthcare systems may experience lower crude death rates.
- Environmental Factors: Natural disasters, pollution, and other environmental hazards can significantly impact mortality rates.
What are the Limitations of the Crude Death Rate?
While the crude death rate is a useful metric, it does have several limitations:
- Age Distribution: CDR does not account for the age structure of a population, which can lead to misleading interpretations. For instance, two populations may have the same CDR, but different age distributions may reveal significant differences in mortality risks.
- Temporal Variability: CDR can fluctuate over time due to seasonal factors, disease outbreaks, or other sudden changes, making it essential to consider long-term trends rather than short-term snapshots.
- Underreporting: In some regions, deaths may not be accurately recorded, leading to underestimations of the crude death rate.
How Does the Crude Death Rate Impact Public Health Policies?
Public health policies are often shaped by data derived from demographic measures like the crude death rate. Policymakers must consider CDR when planning health initiatives, resource allocation, and emergency response strategies. For instance:
- Targeted Interventions: High crude death rates in specific areas may prompt targeted health programs to address underlying issues, such as access to healthcare or preventive measures.
- Resource Allocation: Understanding mortality trends helps direct funding and resources to the areas that need them most.
- Evaluation of Health Programs: Monitoring changes in CDR following the implementation of health interventions allows for the assessment of their effectiveness.
What is the Relationship Between Crude Death Rate and Life Expectancy?
The crude death rate is inversely related to life expectancy; as the CDR decreases, life expectancy typically increases. This relationship highlights the importance of improving healthcare access, reducing preventable diseases, and addressing social determinants of health. Understanding this correlation can provide valuable insights into the overall health of a population and inform strategies aimed at improving life expectancy.
What Are Some Historical Trends in Crude Death Rates?
Historically, crude death rates have seen significant changes due to various factors, including medical advancements, public health initiatives, and socio-economic developments. Key trends include:
- Decreased Mortality from Infectious Diseases: The introduction of vaccines and antibiotics has led to a significant decline in mortality from infectious diseases.
- Increased Mortality from Non-Communicable Diseases: As populations age and lifestyles change, non-communicable diseases such as heart disease and cancer have become more prevalent.
- Global Disparities: Crude death rates vary significantly between high-income and low-income countries, with the latter often facing higher mortality rates due to limited healthcare access and resources.
In Conclusion: What Insights Can We Gain from the Crude Death Rate?
In conclusion, understanding the crude death rate is essential for gaining insights into the health status of populations, shaping public health policies, and addressing social determinants of health. While it serves as a valuable indicator of mortality, it is crucial to consider its limitations and interpret it alongside other demographic factors. By doing so, we can leverage the crude death rate to inform effective health interventions and improve the overall well-being of populations.
As we continue to monitor and analyze crude death rates, we can better understand the complex interplay of factors that influence mortality and work towards creating healthier societies.
Article Recommendations
- The Ultimate Guide To Seann William Scott From Stifler To A Star
- The Ultimate Jameliz Benitez Onlyfans Experience Uncensored Photos And Videos
- The Definitive Guide To Judd Nelson Exploring The Life And Legacy Of A Hollywood Icon