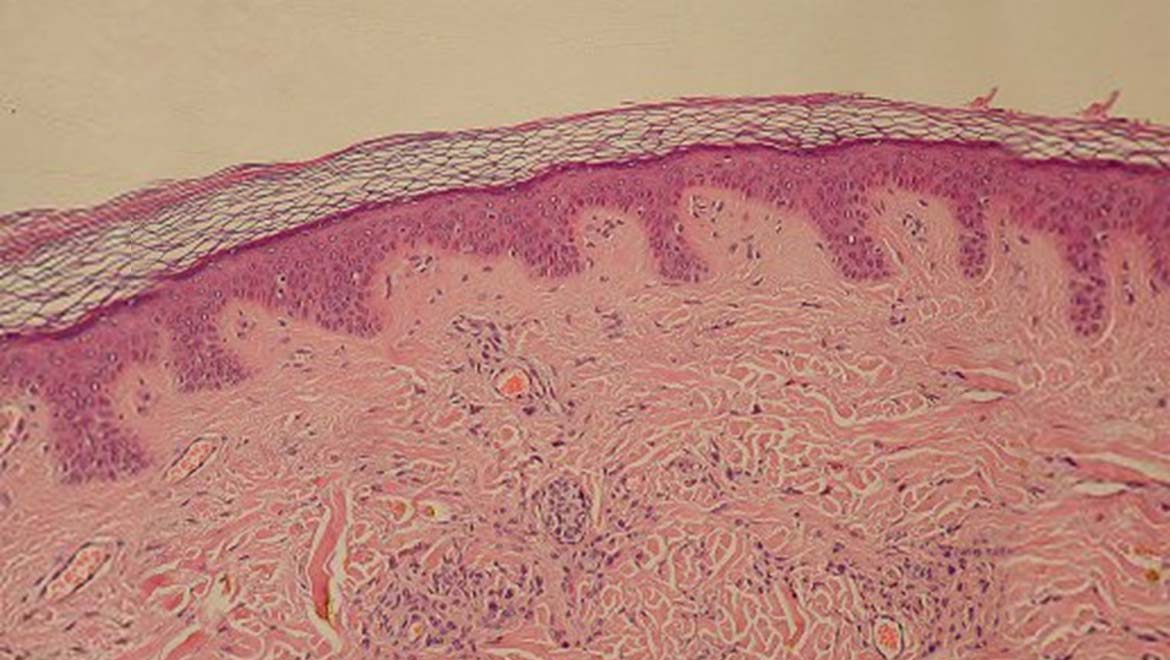
The human body is a complex and intricate system, comprised of various organs that work harmoniously to maintain our health and well-being. Among these organs, one stands out due to its sheer size and multifunctional capabilities: the skin. The largest organ in the body plays a critical role in our everyday lives, serving as a protective barrier, regulating temperature, and providing sensory information. It is fascinating to consider how this remarkable organ is often overlooked, despite its vital functions. Understanding the largest organ in the body can enhance our appreciation for its role in our overall health and highlight the importance of proper skin care.
Our skin, the largest organ in the body, is not just a simple covering; it's a dynamic structure composed of multiple layers, each with specific functions. From the epidermis, which serves as the first line of defense, to the dermis, which houses blood vessels, hair follicles, and sweat glands, every layer of skin contributes to our body's homeostasis. The skin's ability to heal itself and adapt to environmental changes is a testament to its complexity and resilience.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the largest organ in the body, exploring its anatomy, functions, and the common conditions that can affect it. We'll also discuss how to maintain skin health and what you can do to protect this essential organ from damage. By the end of this exploration, you will have a better understanding of why the skin deserves our attention and care.
What is the Anatomy of the Largest Organ in the Body?
The skin is made up of three primary layers:
- Epidermis: The outermost layer, which provides a waterproof barrier and skin tone.
- Dermis: The middle layer that contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
- Hypodermis (subcutaneous layer): The innermost layer made of fat and connective tissue that helps insulate the body and absorb shock.
How Does the Largest Organ in the Body Protect Us?
The skin serves several crucial protective functions, including:
- Acting as a barrier against pathogens, bacteria, and environmental toxins.
- Regulating body temperature through sweat production and blood vessel dilation.
- Preventing dehydration by reducing water loss.
What Role Does the Largest Organ in the Body Play in Sensation?
The skin is equipped with a network of nerve endings that allow us to feel sensations such as touch, heat, cold, and pain. This sensory information is crucial for interacting with our environment and protecting us from injury. The different types of sensory receptors found in the skin include:
- Mechanoreceptors: For detecting pressure and vibration.
- Thermoreceptors: For sensing temperature changes.
- Nociceptors: For detecting pain.
What Common Conditions Affect the Largest Organ in the Body?
Despite its resilience, the skin can be susceptible to various conditions, including:
- Acne: A common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells.
- Eczema: An inflammatory condition characterized by itchy, red, and dry skin.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune disorder causing rapid skin cell production leading to scaling and inflammation.
- Skin cancer: A serious condition that can develop from abnormal skin cell growth.
How Can We Maintain the Health of the Largest Organ in the Body?
Taking care of the skin is essential for preventing various conditions and maintaining its overall health. Here are some tips:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the skin hydrated from the inside out.
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
- Gentle Cleansing: Use mild soaps and cleansers to avoid stripping the skin of its natural oils.
- Moisturizing: Apply moisturizer daily to maintain skin hydration.
What Lifestyle Factors Influence the Largest Organ in the Body?
Various lifestyle factors can have a significant impact on skin health, including:
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can promote skin health.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke can damage collagen and elastin, leading to premature aging.
- Stress: High levels of stress can trigger skin conditions like acne and eczema.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for skin repair and regeneration.
Conclusion: Why Should We Care About the Largest Organ in the Body?
The skin, as the largest organ in the body, plays a vital role in protecting us, regulating our internal environment, and providing sensory feedback. By understanding its functions and maintaining its health, we can ensure that our largest organ continues to serve us well throughout our lives. Investing time in skincare and adopting healthy lifestyle choices will not only enhance our skin's appearance but also improve our overall health and well-being.
Ultimately, the largest organ in the body deserves our attention and care, as it is a reflection of our lifestyle choices and overall health. Let's prioritize our skin and appreciate the remarkable functions it performs every single day!
Article Recommendations
- The Notorious Case Of Thomas Sullivan A Murder Most Foul
- The Ultimate Guide To Leslie Easterbrook A Hollywood Icon
- The Ultimate Goojara Movies Experience Explore A World Of Entertainment